Describe the Trichromatic Theory of Color Vision.
The trichromatic theory proposes that color vision is based on there being three elements in our visual system that respond differently to different wavelengths. Any 3 lights that span the vector space of the cone absorption spectra can match any color percept.

Color And Depth Perception Introduction To Psychology
One of the more important empirical aspects of this theory is that it is possible to match all of the colors in the visible spectrum by appropriate mixing of three primary colors.

. Although complementary colors theory is the most up-to-date the trichromatic theory and opponent process theory do help account for the complexity of color vision. Describe trichromatic theory and opponent-process theory of color vision including theobservations on which it is based and the physiological basis of each theory. Trichromatic theory of color perception.
Red green and yellow B. Red green and blue. The trichromatic theory states that our cones allow us to see details in normal light conditions as well as color.
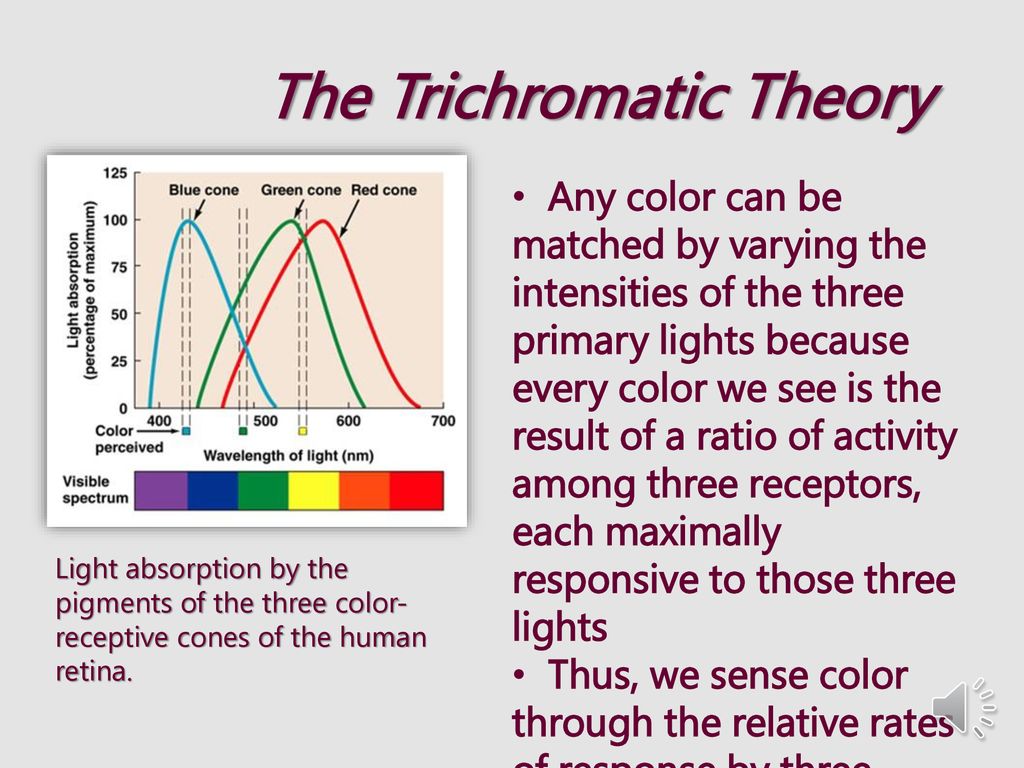
Trichromatic Theory of Vision Doctor Thomas Young proposed this theory in 1801. Based on the premise that there are three classes of cone receptors subserving color vision. Describe the trichromatic theory of color vision and its relationship to the three classes of cones that we have.
The trichromatic theory explains how the three types of cones detect different light wavelengths. Characterized by absorpotion spectra basis vectors for color perception Color matching. This trichromatic theory is not new.
Currently the trichromatic theory of color vision states that the color of any light is determined by the output of the three cone systems in our. Color vision is mediated by the activity across the three groups of cones trough. Each of these cone types is maximally sensitive to a slightly different wavelength of light.
This theory suggested that color vision is based on three primary colors. One of the more important empirical aspects of this theory is that it is possible to match all of the colors in the visible spectrum by appropriate mixing of three primary colors. Red green and blue D.
Black brown and white. The Trichromatic Theory of Colour Vision Young Helmholtz states that colour vision depends on the activity of 3 different receptor mechanisms. The trichromatic theory of color vision states that humans have three types of receptors within the eye that vary in sensitivity to different light wavelengths.
Normal-sighted individuals have three different types of cones that mediate color vision. Lastly watch the video onsynaethesia below and discuss what it means to say that. The trichromatic theory of color vision is based on the premise that there are three classes of cone receptors subserving color vision.
Trichromatic Theory of Colour Vision is our perception of colour is determined by the ratio of activity in three receptor mechanisms with different spectral sensitivities. The proposal said that the eye could perceive light by three color-sensitive receptors arrayed along the inner wall of the eye the retina. The three receptors are usually associated with the colors red green and blue.
Lastly watch the video on synaethesia below and discuss what it means to say that color is created by the nervous system. The cones in the retina are what give color vision. The trichromatic theory of color vision is a theory that states there are three different color receptors in the retina.
We have cones that respond preferentially not exclusively for red green and blue Svaetichin 1955. According to the trichromatic theory of color vision the eye has cones sensitive to colors associated with red green and blue. Color is all around us but just how deeply integrated is the phenomenon of color into our senses and neuralpathways.
This theory was developed by Thomas Young and Herman von Helmholtz and thus it is also called the Young-Helmholtz theory. Instead Hering believed that the way we view colors is based on a system of opposing colors. Color vision summary light source.
According to the Young-Helmholtz trichromatic theory of color vision shown in Figure 1 all colors in the spectrum can be produced by combining red green and blue. This theory has a very long history dating back to the 18th century. Coordination of motion information with visual information that allows you to maintain your gaze on.
Green purple and red C. The three types of cones are each. In the trichromatic theory they proposed that the retina is comprised of three distinct types of cones or color-sensitive photoreceptors.
Defined by illuminant power spectrum Trichromatic color vision relies on 3 cones. Instructor Resource Schwartz Sensation and Perception 2e SAGE Publications Inc 2019 Difficulty Level. Trichromatic theory According to the trichromatic theory of colour vision also known as the Young-Helmholtz theory of colour vision there are three receptors in the retina that are responsible for the perception of colour.
It dates back to the early 19th century Young 1802. As evidence for the theory proponents cited the fact that all the colors that can be perceived can be created by mixing three colored lights that differ in wave length. This theory evolved as scientists gained knowledge of the cones in the retina.
The first trichromatic theory is based on the idea that the visual system is maximally responsive to three colors and that color vision is a result of the combination of differential responses of these three components. Lowest point of a wave vestibulo-ocular reflex. The process of color vision starts in the retina according to the Trichromatic Theory.
The Trichromatic Theory of Color Vision. Describe trichromatic theory and opponent-process theory of color vision including the observations on which it is based and the physiological basis of each theory.

Trichromatic Theory Of Color Vision What Is Helmholtz Trichromatic Theory Video Lesson Transcript Study Com

No comments for "Describe the Trichromatic Theory of Color Vision."
Post a Comment